ETag Overview
With ETag support now available in the Draft API, you can safely update stories by ensuring you’re working on the intended version.
Background
When you are changing a story, the typical workflow is to first call the Draft API to get the most recent revision. The response will include an etag field.
You then submit your updates, along with an If-Match header with the same ETag.
The Draft API does a check to verify that the ETag you submitted is the most recent version of the story, applies the update, and makes the new revision.
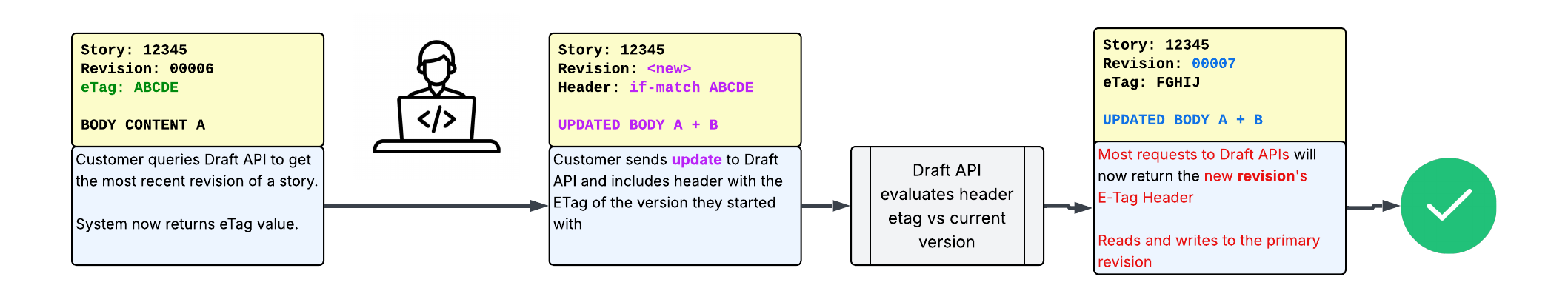
The check ensures that a faster-running process doesn’t apply an update that you may overwrite.
In that scenario, the flow looks like the following:
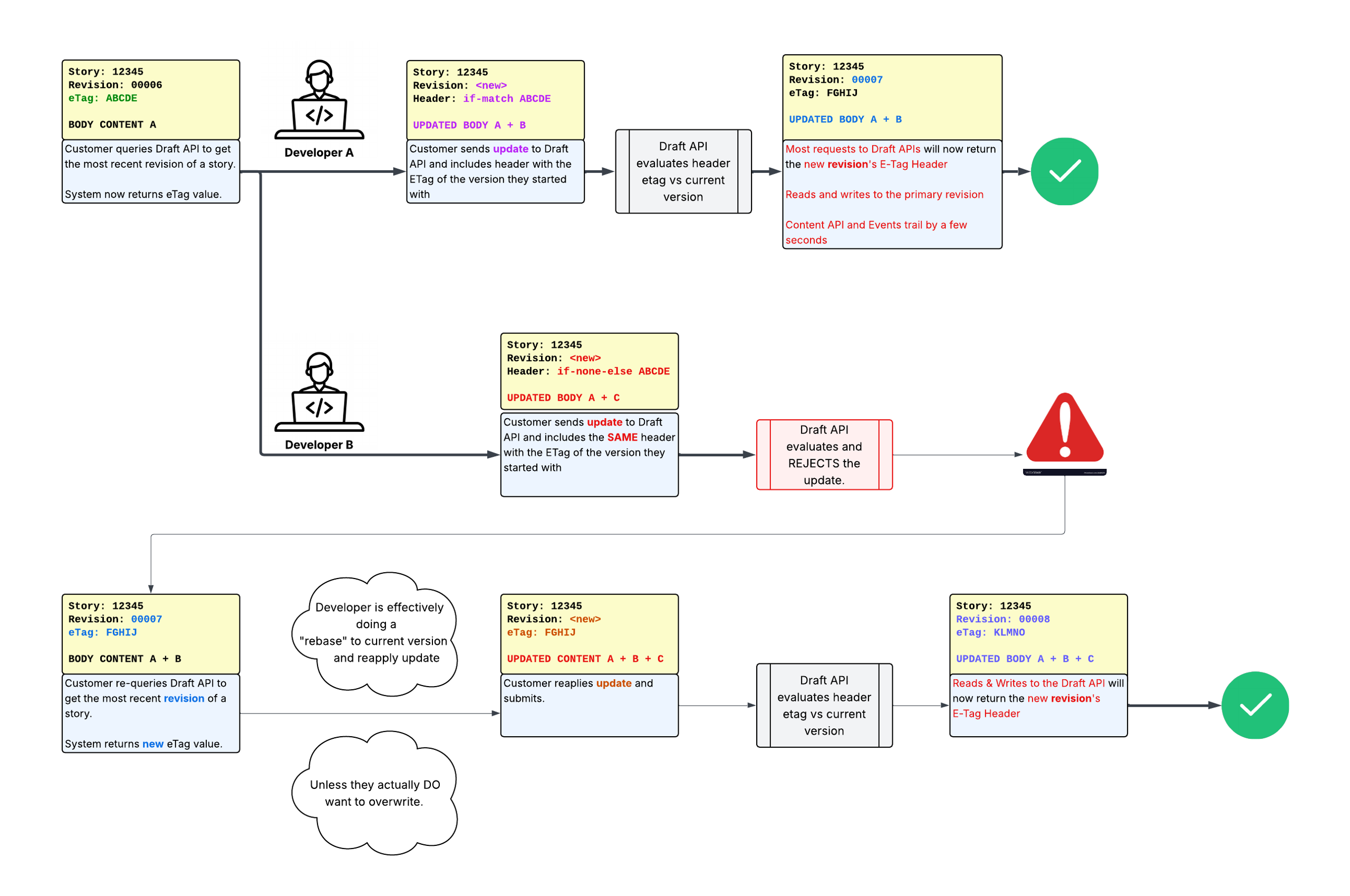
The key point is that your code should handle errors when you submit an update with the ETag and get a rejection. In those cases, you should:
- Update the original document
- Reapply your changes
- Resubmit your updates
What ETags will NOT do
- Merge your change if you skip
If-None-Matchheader - Help with
POST,PUT,PATCHorDELETEcalls - Help with chunked (binary) uploads
- If your process is long-running with multiple updates, you may need to create a queue on your side and write your own code to check the current version.
FAQ
Can I get an ETag from the Content API?
No, the Draft API and its underlying database serve as the system of record for all content. We rapidly synchronize updates out to the Content API and View API for events, indexing and content retrieval, but for larger volume updates, you should check the Draft API via /draft/v1/story/{id}/revision/draft.

